
What is OCT?
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of medical imaging, Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has emerged as a groundbreaking technology, revolutionizing diagnostic capabilities in ophthalmology and beyond. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of OCT, exploring its principles, applications, and the transformative impact it has on healthcare.
What is OCT?
Optical Coherence Tomography is a non-invasive imaging technique that enables high-resolution cross-sectional imaging of biological tissues. It utilizes the principles of low-coherence interferometry to capture detailed images with remarkable precision. Unlike traditional imaging methods, OCT provides real-time, three-dimensional visualization, offering clinicians unparalleled insights into the microstructures of tissues.
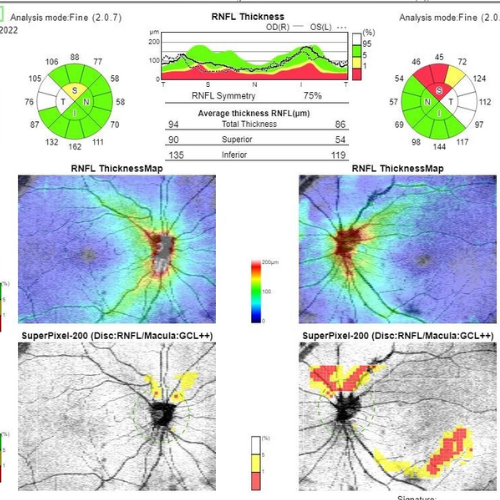
How OCT Works
At its core, OCT employs a beam of low-coherence light, typically in the infrared spectrum, to penetrate tissues. The reflected light is then compared with a reference beam, creating interference patterns. By analyzing the interference patterns, OCT generates detailed cross-sectional images, allowing for the visualization of tissue layers and structures.
Key Components of OCT System
Light Source: The selection of an appropriate light source is critical for optimal imaging. Broadband light sources enhance resolution and penetration depth.
Interferometer: OCT utilizes Michelson interferometry to measure the delay between the reference and sample arms accurately.
Detector: High-performance detectors capture the interference patterns, converting them into digital signals for image reconstruction
Ophthalmology
OCT has revolutionized ophthalmic diagnostics by enabling detailed imaging of the retina, optic nerve, and cornea. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring conditions such as macular degeneration, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy.
Cardiovascular Imaging
In cardiology, OCT provides intricate insights into coronary artery structures, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. It has become an invaluable tool for guiding interventional procedures.
Advantages of OCT
High Resolution: OCT offers micron-level resolution, surpassing many traditional imaging methods.
Non-Invasiveness: As a non-invasive technique, OCT reduces patient discomfort and the risk of complications.
Real-Time Imaging: The ability to obtain real-time images enhances the efficiency of diagnostic and interventional procedures.
Future Trends in OCT
As technology advances, the future of OCT holds exciting possibilities. Integration with artificial intelligence for image analysis, enhanced portability, and expanded applications across medical specialties are anticipated developments.
This comprehensive guide serves as an authoritative resource for understanding OCT, positioning itself as a valuable asset for both medical professionals and those seeking insights into this transformative imaging technology.
